Case-based TB surveillance. In: Global tuberculosis report 2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2021
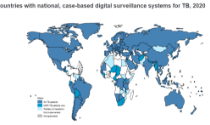
Digital, case-based, real-time surveillance for TB: status of progress Tuberculosis (TB) surveillance is the continuous and systematic collection, analysis and reporting of data related to TB infection and TB disease in the population. To support countries to implement national surveillance systems for TB in a consistent and comparable way worldwide, the World Health Organization (WHO) has, since the mid-1990s, provided guidance with standardized definitions, forms, registers and reports (1). There were major updates to this guidance in 2006 (2) and 2013 (3).
Read MoreAgarwal S, Jalan M, Pandya S, Ferguson R, Moustafa D, Ng C, et al. Digital solutions for COVID-19 response: an assessment of digital tools for rapid scale-up for case management and contact tracing. Baltimore: John Hopkins Global mHealth Initiative – Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health; 2020
Read MoreNikshay reports: dashboard. Delhi: Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India
Read MoreTuberculosis data. In: Global Tuberculosis Programme. Geneva: World Health Organization
Global Tuberculosis Programme: The WHO Global Tuberculosis Programme works towards the goal of a world free of TB, with zero deaths, disease and suffering due to the disease. The team’s mission is to lead and guide the global effort to end the TB epidemic through universal access to people-centred prevention and care, multisectoral action and innovation.
Read MoreWHO Toolkit for routine health information systems data. Modules. Geneva: World Health Organization
WHO Toolkit for Routine Health Information Systems Data This effort is led by WHO and its Collaborating Centre on Innovation and Implementation Research for Health Information System Strengthening at the University of Oslo, with support from Health Data Collaborative partners, including UNICEF, Global Fund, GAVI and PEPFAR. For questions or comments, please contact healthinfo@who.int Health service data are essential for patient management, facility management, disease surveillance and monitoring of service provision and resource use. Countries also need reliable facility data to assess the performance of their health services as they work towards the UHC targets and the SDGs.
Read MoreA new digital platform for timely analysis and use of TB data. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019
The WHO Global TB Programme has developed and is supporting country implementation of a new digital platform to store, analyze and visualize national and subnational TB surveillance data. The platform will facilitate timely planning and programmatic action.
Read MoreMapping the technology landscape of national TB programs: report. Geneva: The Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria; 2021
Harnessing the power of digital health technologies is essential to driving progress in the fight against tuberculosis (TB). The COVID-19 pandemic has further underlined the importance of digital tools and international cooperation and collaboration for global health. This report, produced in collaboration with our partners Microsoft and the Stop TB Partnership, shows that there is a need for countries, donors and procurers to use their purchasing power and influence to promote market shaping for these tools. Shortcomings of financing, policies and appropriate resources need to be addressed in order to make digital health tools available in each country and realize the full potential of existing innovations. Different countries use different infrastructures as the backbone of their health systems, making it difficult to distribute new tools and digital subsystems globally.
Read MoreStop TB field guide 9: strengthening information systems and linkages to care. Geneva: Stop TB Partnership; 2018
This document is one in a series of 11 field guides produced by Stop TB Partnership in collaboration with the Global Fund to Fight AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria, KIT Royal Tropical Institute, Interactive Research and Development Global (IRD), and multiple global experts and implementation partners.
Read MoreTB Data Hub – Enhance data. Expand data analysis. End tuberculosis. Chapel Hill: TB DIAH Project, University of North Carolina
The TB Data, Impact Assessment and Communications Hub (TB DIAH) project, funded by the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), is associated with USAID’s Global Accelerator to End Tuberculosis (TB). The Accelerator is USAID’s new business model to focus on performance-based measures for combating TB. We will work to strengthen the capacity of national TB programs to reach every person with TB, including vulnerable groups; cure those who need treatment; and prevent the spread of new infections. TB DIAH will also help foster country commitment to policies and action for inclusive and accountable governance of TB programs with strong information systems, infrastructure and financial support, and participation of all of civil society.
Read More
Guideline: Recommendations on Digital Interventions for Health System Strengthening
The key aim of this guideline is to present recommendations based on a critical evaluation of the evidence on emerging digital health interventions that are contributing to health system improvements, based on an assessment of the benefits, harms, acceptability, feasibility, resource use and equity considerations. This guideline urges readers to recognize that digital health interventions are not a substitute for functioning health systems, and that there are significant limitations to what digital health is able to address.
Read More




















































 Case-Based
Case-Based
 Aggregated
Aggregated


 South Africa
South Africa